Electromagnetic Brake
Electromagnetic Brake
Electromagnetic brakes are the brakes working on the electric power & magnetic power. The works on the principle of electromagnetism. These are totally frictionless. Due to this they are more durable & have a longer life span. Less maintenance is there. These brakes are an excellent replacement on the convectional brakes due to their many advantages. The reason for implementing this brake in automobiles is to reduce wear in brakes as it frictionless. Therefore there will also be no heat loss. It can be used in heavy vehicles as well as in light vehicles.
The electromagnetic brakes are much effective than conventional brakes & the time taken for the application of brakes are also smaller. There is very few need for lubrication. Electromagnetic brakes give much better performance with less cost which is today’s need. There are also many more advantages of Electromagnetic brakes. That’s why electromagnetic brakes are an excellent replacement on conventional brakes.
Electromagnetic brakes are of today’s automobiles. An electromagnetic braking system for automobiles like cars, and effective braking system. And, by using these electromagnetic brakes, we can increase the life of the braking unit. The working principle of this system is that when the magnetic flux passes through and perpendicular to the rotating wheel the eddy current flows opposite to the rotating wheel/rotor direction. This eddy current trying to stop the rotating wheel or rotor. This results in the rotating wheel or rotor come to rest/ neutral.
HISTORY
It is found that electromagnetic brakes can develop a negative power which represents nearly twice the maximum power output of a typical engine, and at least three times the braking power of an exhaust brake. (Reverdin 1994). This performance of electromagnetic brakes makes them a much more competitive candidate for alternative retardation equipment compared with other retarders. By using the electromagnetic brakes are supplementary retardation equipment, the friction brakes can be used less frequently, and therefore practically never reach high temperatures. The brake linings would last considerably longer before requiring maintenance and the potentially “brake fade” problem could be avoided.
In research conducted by a truck manufacturer, it was proved that the electromagnetic brake assumed 80% of the duty which would otherwise have been demanded of the regular service brake (Reverdin 1974). Furthermore, the electromagnetic brakes prevent the danger that can arise from the prolonged use of brake beyond their capability to dissipate heat.
This is most likely to occur while a vehicle descending a long gradient at high speed. In A study with a vehicle with 5 axles and weighing 40 tons powered by a powered by an engine of 310 b.h.p travelling down a gradient of 6% at a steady speed between 35 and 40 m.h.p, it can be calculated that the braking power necessary to maintain this speed at the order of 450 hp. The brakes, therefore, would have to absorb 300 hp, meaning that each brake in the 5 axles must absorb 30 hp, that a friction brake can normally absorb with self-destruction.
The magnetic brake is well suited to such conditions since it will independently absorb more than 300 hp (Reverdin 1974). It, therefore, can exceed the requirements of continuous uninterrupted braking, leaving the friction brakes cool and ready for emergency braking in total safety.
The installation of an electromagnetic brake is not very difficult if there is enough space between the gearbox and the rear axle. If did not need a subsidiary cooling system. It relays on the efficiency of engine components for its use, so do exhaust and hydrokinetic brakes. The exhaust brake is an on/off the device and hydrokinetic brakes have a very complex control system. The electromagnetic brake control system is an electric switching system which gives it superior controllability.
CONSTRUCTION
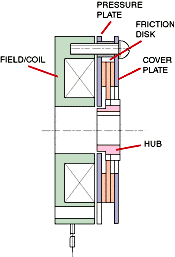
The construction of the electromagnetic braking system is very simple. The parts needed for the construction are electromagnetic, rheostat, sensors and magnetic insulator. A cylindrical ring shaped electromagnet with winding is placed parallel to rotating wheel disc/ rotor. The electromagnet is fixed, like as stator and coils are wounded along the electromagnet. These coils are connected with an electrical circuit containing one rheostat which is connected with the brake pedal. And the rheostat is used to control the current flowing is used to control the magnetic flux. And also it is used to prevent the magnetization of other parts like axle and it acts as a support frame for the electromagnet. The sensor used to indicate the disconnection in the whole circuit. If there is any error it gives an alert, so we can avoid an accident.
WORKING PRINCIPLE
The working principle of the electric retarder is based on the creation of eddy currents within a metal disc rotating between two electromagnets, which set up a force opposing the rotation of the discs. If the electromagnet is not energized, the rotation of the disc free and accelerates uniformly under the action of the weight to which its shaft is connected.
When the electromagnet is energized, the rotation of the disc is retarded and the energy absorbed appears as heating of the discs. If the current exciting the electromagnet is varied by a rheostat, the raking force varies in direct proportion of the value of the current. The development of this invention began when the French company Thelma, associated with Raoul Sarasin, developed and marketed several generations of electric brake based on the functioning principle described above. A typical retarder consists of stator and rotor. The stator hold 16 induction coils, energized separately in a group of four. The coils are made up of varnished aluminium wire mounted in epoxy resin.
The stator assembly is supported resiliently through anti-vibration mountings on the chassis frame of the vehicle. The rotor is made up of two discs, which provide the braking force when subjected to the electromagnetic influence when the coil is excited. Carefully design of the fins, which are integral to the disc, permit independent cooling of the arrangement.
ADVANTAGES
1. Electromagnetic brakes can develop a negative power which represents nearly twice the maximum power output of a typical engine.
2. Electromagnetic brakes work in a relatively cool condition and satisfy all
The energy requirements of braking at high speeds, completely without the use of friction. Due to its specific installation location (transmission line of rigid vehicles), electromagnetic brakes have better heat dissipation capability to avoid problems that friction brakes face times the braking power of an exhaust brake.
3. Electromagnetic brakes have been used as supplementary retardation equipment in addition to the regular friction brakes on heavy vehicles.
4. Electromagnetic brakes have great braking efficiency and has the potential to regain energy lost in braking.
5. Its component cost is less.
DISADVANTAGES
1. The installation of an electromagnetic brake is very difficult if there is
Not enough space between the gearbox and the rear axle.
2. Need a separate compressor.
3. Maintenance of the equipment components such as hoses, valves have to done periodically.
4. It cannot use grease or oil.
APPLICATIONS
1. Used in the crane control system.
2. Used in winch controlling.
3. Used in lift controlling.
4. Used in automatic purpose.
Lots of new technologies are arriving in the world. They create a lot of effects. Most industries got their new faces due to this arrival of technologies. The automobile industry is also one of them. There is a boom in World’s automobile industry. So lots of research is also going here. As an important part of the automobile, there are also innovations in brakes. Electromagnetic brake is one of them.
Electromagnetic braking for automobiles like cars, and effective braking system. And, by using these electromagnetic brakes, we can increase the life of the braking unit. The working principle of this system is that when the electromagnetic flux passes through and perpendicular to the rotating wheel the eddy current is induced in the rotating wheel or rotor. This eddy current flows opposite to the rotating wheel. This eddy current tries to stop the rotating wheel or rotor. This results in the rotating wheel or rotor come to rest.




Comments
Post a Comment